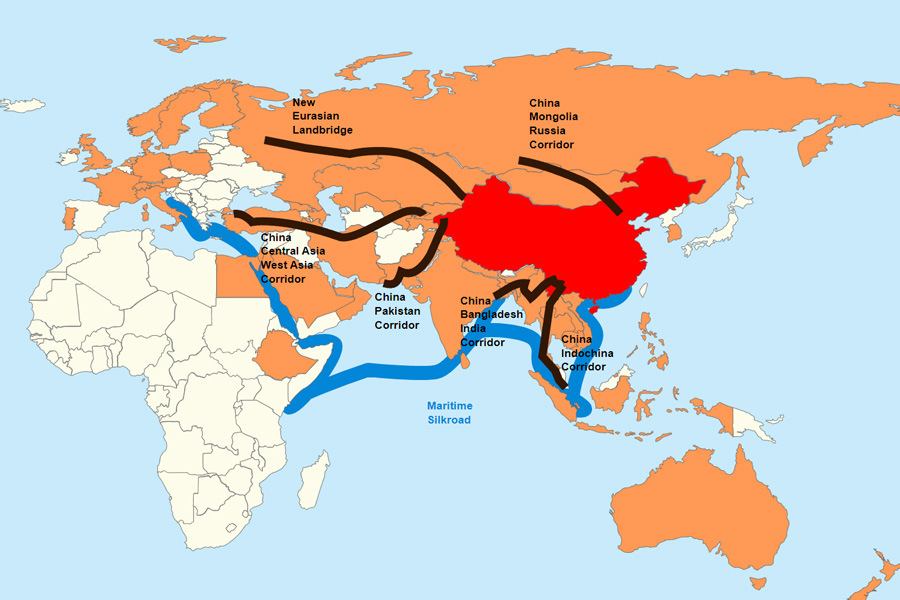
The paper examines whether the BRI is certainly a worthwhile initiative for Asian economics by associating the relative estimation powers of the two mentioned techniques using bilateral trade flow from 1990 to 2019 of 32 Asian partner countries.
Authors
Sunetra Ghatak, Assistant Professor, Jindal School of Government and Public Policy, O.P. Jindal Global University, Sonipat, Haryana, India.
Sayantan Roy, School of Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi-110067, India.
Summary
International trade and association are the key contributors to economic integration and cohesion. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is an auspicious development initiation taken by the Chinese government to endorse the logistics and infrastructure expansion under the One Belt One Road (OBOR) so that economic cohesion can be achieved between China and its trading partners.
After half a decade of the BRI initiative, arguments have been elevated whether this remained profitable for the connected partner countries in the long run. Against this backdrop, this paper tries to estimate the trade performance of participating and connecting country’s using the traditional gravity model along with neural network model.
The paper is set to examine whether the BRI is certainly a worthwhile initiative for Asian economics by associating the relative estimation powers of the two mentioned techniques using bilateral trade flow from 1990 to 2019 of 32 Asian partner countries.
Published in: Chakraborti, A., Haven, E., Patra, S., Singh, N. (eds) Quantum Decision Theory and Complexity Modelling in Economics and Public Policy. New Economic Windows. Springer, Cham
To read the full chapter, please click here.

